Editor’s Note: A version of this story appeared in CNN’s Wonder Theory newsletter. To receive it in your inbox, Sign up for free here.
As Earth Day approaches and the Wonder Theory newsletter celebrates three years of arriving in your inboxes, I look to the future with hope.
We all start somewhere. Encouragement and the search for knowledge help us grow. When Jane Goodall was a little girl, her mother nurtured the celebrated primatologist’s love for the living world.
Now 90, Goodall nurtures that same appreciation through her Roots & Shoots program, which empowers young people to create change in their communities around the world.
Even as the world changes in response to the climate crisis, Goodall remains hopeful that humanity can save the planet.
“Don’t forget that you as an individual make an impact on the environment every day,” Goodall told CNN recently. “And it’s up to you to choose what kind of impact you make.”
Secrets of the ocean
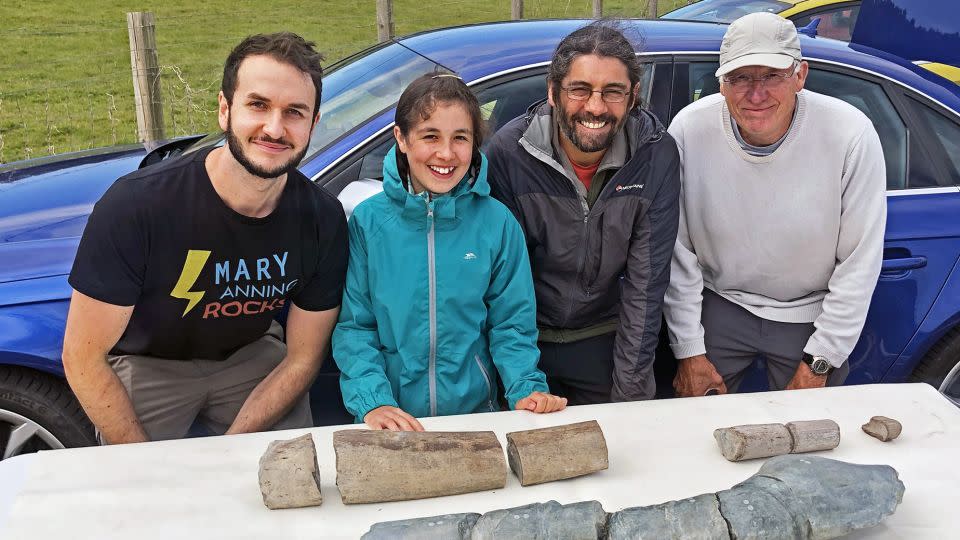

In May 2020, Ruby Reynolds, then 11, and her father, Justin, were looking for fossils on a beach in Somerset, along the English coast, when they spotted something unusual.
Now reassembled with the help of experts, the fossils found by Ruby have revealed the jaw of a giant ichthyosaur that roamed the seas 202 million years ago. And when it came to size, the marine reptile probably rivaled the blue whalecurrently the largest living animal.
“It was really cool to discover part of this giant ichthyosaur. I am very proud to have participated in a scientific discovery like this,” she said.
Meanwhile, in India, paleontologists at the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee have unearthed evidence of a different massive reptile: a prehistoric snake that was longer than a school bus.
A long time ago
Archaeologists have pieced together the puzzle of the dramatic collapse of a dynasty after finding burned remains inside an ancient Mayan pyramid in Guatemala.
The research team discovered the charred bones of four adults, as well as luxurious adornments and weaponsin a room below a temple, leading them to believe that the people were of royal lineage.
It’s likely that a new type of leader emerged during a time of political and social change for the Maya, and the bones were burned as a sign of intentional desecration, the team said.
Separately, two 5,500-year-old skeletons recovered from an archaeological site in southwestern France belonged to women who were likely buried alive in a sacrificial rite. using an Italian mafia-style form of torture.
Other worlds
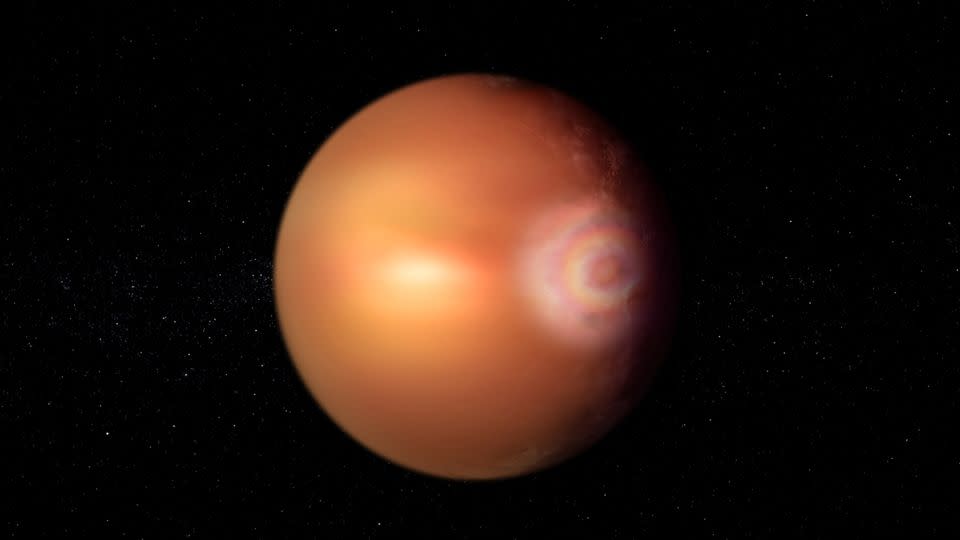

For the first time, astronomers have detected a rainbow-like effect called glory on a planet outside our solar system.
Scientists using the Cheops space telescope noticed an unexpected glow in the atmosphere on WASP-76b. An artistic illustration depicts the phenomenon, which appears as colorful, concentric rings of light and has only been observed on Earth and Venus.
The sizzling exoplanet, located 637 light-years away, is also intriguing because it has one side that permanently faces a Sun-like star, raining molten iron from its clouds.
In a different study, scientists discovered that an ancient, cataclysmic collision with another planet created the telltale Bright white heart seen shining on the surface of Pluto.
All over the universe
A star’s unusual wobble led astronomers to what they dubbed the cosmic “sleeping giant” in the Milky Way.
The Gaia space telescope has detected the most massive stellar black hole knownor a black hole formed from the collapse of a giant star in our galaxy.
Called Gaia BH3, the celestial heavyweight has a mass almost 33 times that of our Sun and is just 1,926 light-years away.
Fantastic creatures
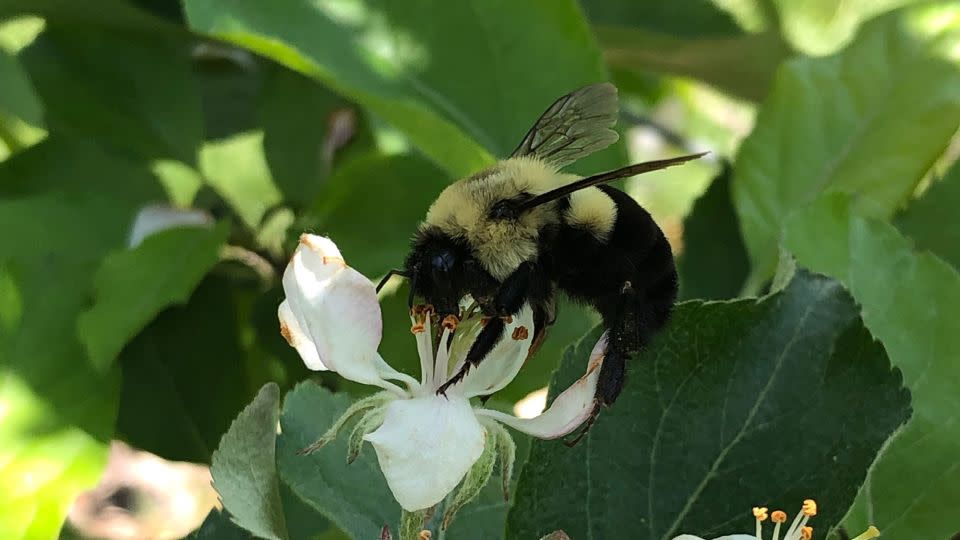


When scientists accidentally submerged a specific type of hibernating bee in water, they made a remarkable discovery: common eastern queen bees can survive underwater for up to a week.
It’s possible that queens, which hibernate alone during the cold season after males and worker bees die, enter a state of suspended growth called diapause, which helps them survive.
Meanwhile, as billions of cicadas are expected to emerge this spring after spending more than a decade underground, scientists hope that some of the insects are manipulated by a zombifying fungus.
The pathogen turns cicadas into “salt shakers of death”, as described by Dr. Matt Kasson, associate professor at West Virginia University.
Explorations
Take a look at these surprising stories:
— Budget cuts threaten the program that could recover rare Mars samples collected by the Perseverance rover. Now, NASA is requesting creative methods to return them to Earth.
— Excavations in South Australia have revealed three new species of giant kangaroos that lived millions of years ago, and one of them was about twice the size of the largest kangaroos alive today.
– NASA expected debris ejected from the International Space Station to burn up in Earth’s atmosphere, but a piece of space junk survived the fiery re-entry process and crushed in a home in Naples, Florida.
— Camels once roamed what is now Canada, but they crossed the Bering Land Bridge 17,000 years ago and completely readapted to live in the desert – and humans can learn from their transformation.
Did you like what you read? Oh, but there’s more. Sign here to get the next issue of Wonder Theory delivered to your inbox, brought to you by CNN Space and Science writers Ashley Strickland It is Katie Hunt. They find wonders on planets beyond our solar system and in discoveries from the ancient world.
For more news and newsletters from CNN, create an account at CNN.com


































