The partial failure of Minnesota’s 114-year-old Rapidan Dam highlights the risks many communities face as the number of dams in disrepair increases and climate change makes rains more frequent and severe.
Before the breach, which caused floodwaters to spread up the bank of the Minnesota River and swallow a house by the sea, local leaders in Blue Earth County, Minnesota, were considering demolishing the old structure or undertaking costly long-term repairs. Regulators deemed the dam a “significant” hazard and it was classified as being in “poor” condition in April 2023, according to the National Inventory of Dams.
Nearly 4,100 dams are categorized at the same risk level and condition — or worse — according to an NBC News analysis of inventory data. Every state has at least one of these dams. Ohio has the highest number, 373.
As a whole, America’s dams — more than 91,000 in total – they are getting older. Many need expensive rehabilitation. Few were designed for the current climate, with a warmer atmosphere that can hold – and dump – more water. The number of people living in flood zones below these dams continues to grow.
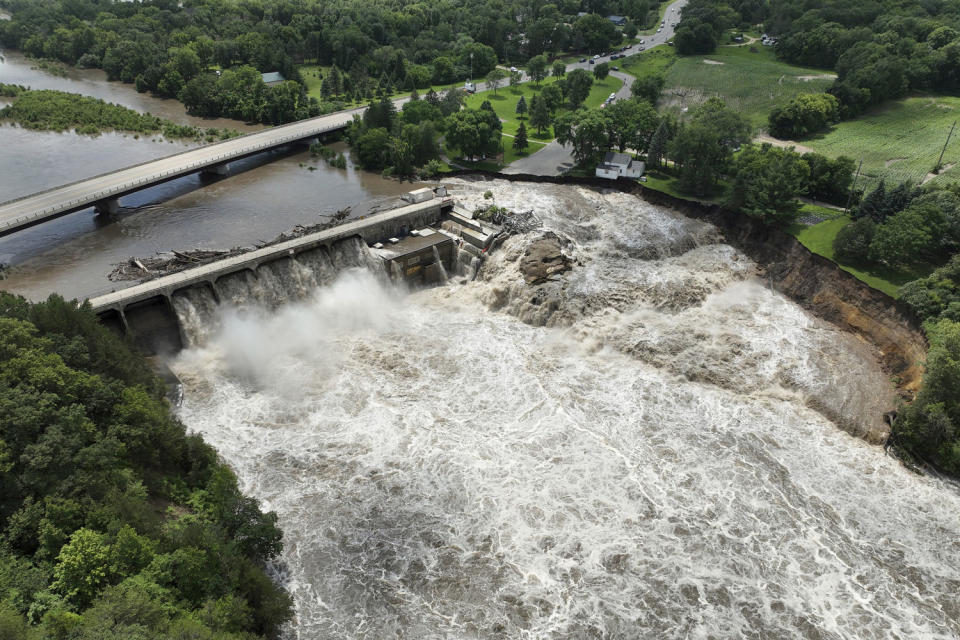

The average age of a dam in the US is 57 years and dam safety experts say the pace of investment has been too slow to maintain the infrastructure up to the standards for which it was built, let alone the worsening climate risks.
“It’s falling behind,” said Sharon Tapia, president of the Association of State Dam Safety Officials. “We are in a situation where we are seeing more and more dams needing to be rehabilitated or repaired to meet current standards.”
The association estimated in a report last year that US$157.5 billion would be needed to match US non-federal dams. This only concerns current safety standards – it does not take into account improvements to address additional and future risks from climate change, she said.
President Joe Biden’s 2021 Infrastructure Blueprint Included US$3 billion for dam safety projects – a small slice compared to the overall need.
It’s too early for scientists to say whether global warming played a role in the Rapidan Dam’s partial failure, but it has made the conditions that led to it more likely.
For every degree Fahrenheit of warming, the atmosphere can retain and deliver about 3% to 4% more moisture, giving storms a stronger impact and making rainfall totals that were once considered rare much more common. This, in turn, increases the risk of devastating floods.
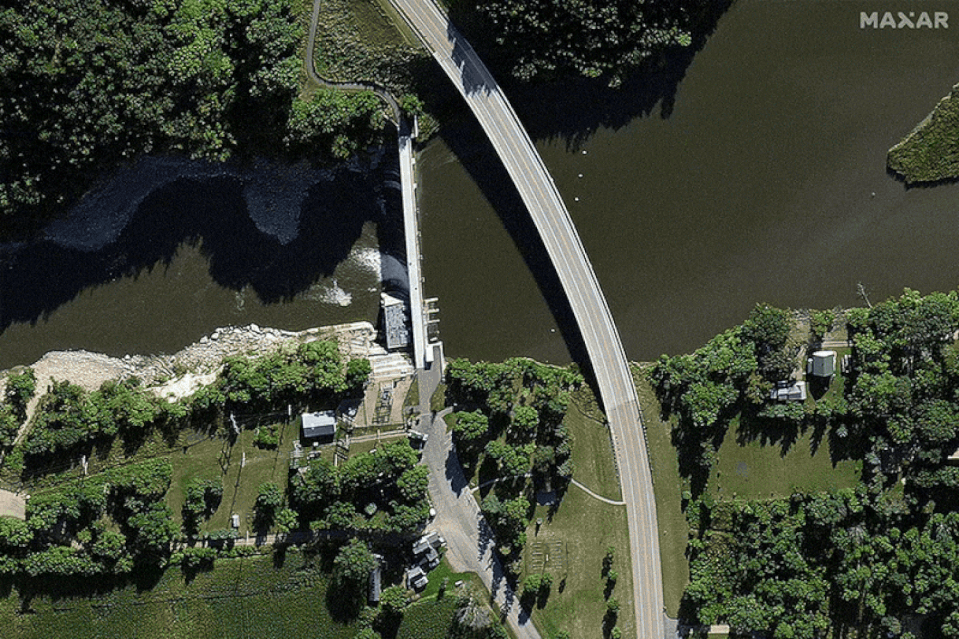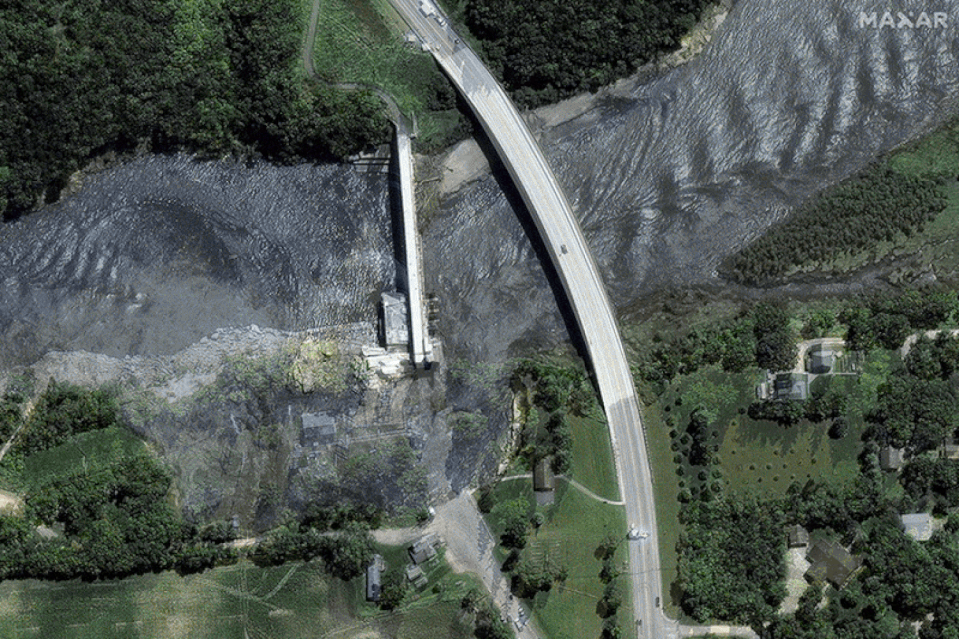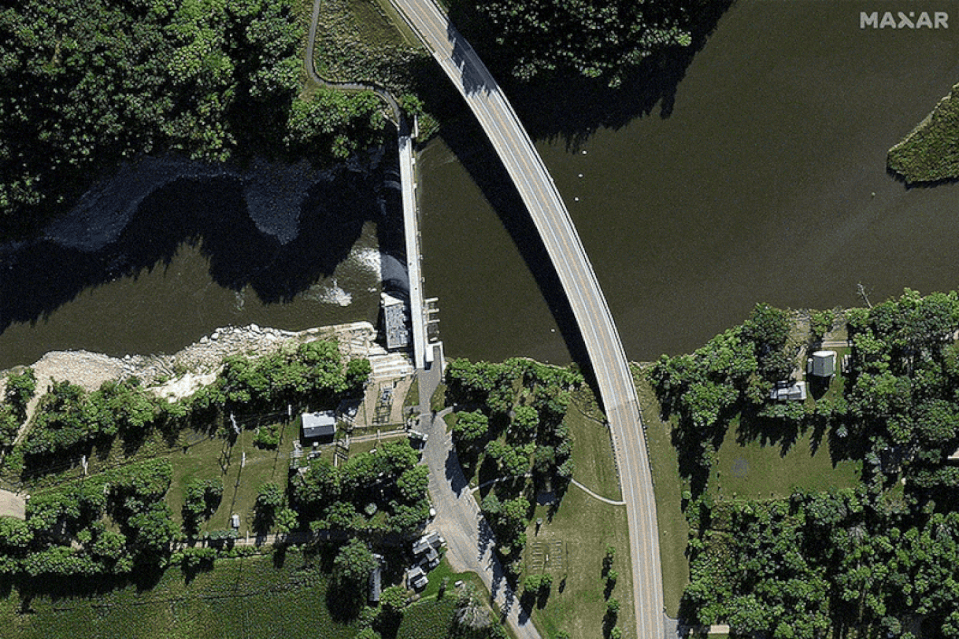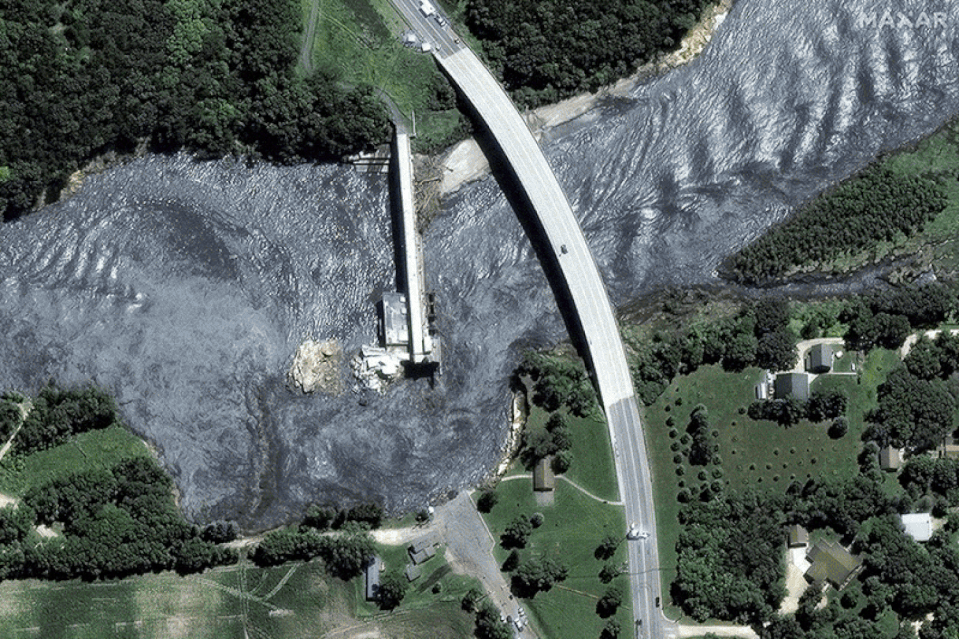

The Rapidan Dam, built in 1910 and managed by Blue Earth County, was described on the county website as being in a “state of disrepair.” After the 2019 and 2020 floods, a power generation company stopped leasing the dam, leaving it without a hydroelectric operator.
But the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, which regulates the dam, wasn’t overly concerned about the structure’s integrity until last month. According to FERC documents, the dam was inspected on May 21 and “found to be in generally satisfactory condition.”
“No major deficiencies in dam safety were observed that would require immediate corrective action,” the letter said, although it mentioned severe concrete deterioration, exposed rebar and cracks that should be monitored closely.
The inspection, analysis of the safety and stability of the structure, was separate from the evaluation of the National Inventory of Dams, which considers the full performance of the project, said a FERC spokesperson.
Blue Earth County officials were weighing whether to remove the damat a cost of more than US$82 million, or to repair for around $15 million. Both options had drawbacks: Repairs could last only 40 years, while removal could take five years to plan and obtain permits, according to 2021 engineering documents. A county spokesperson said officials were unable to answer questions as well as provide updates at press conferences. .
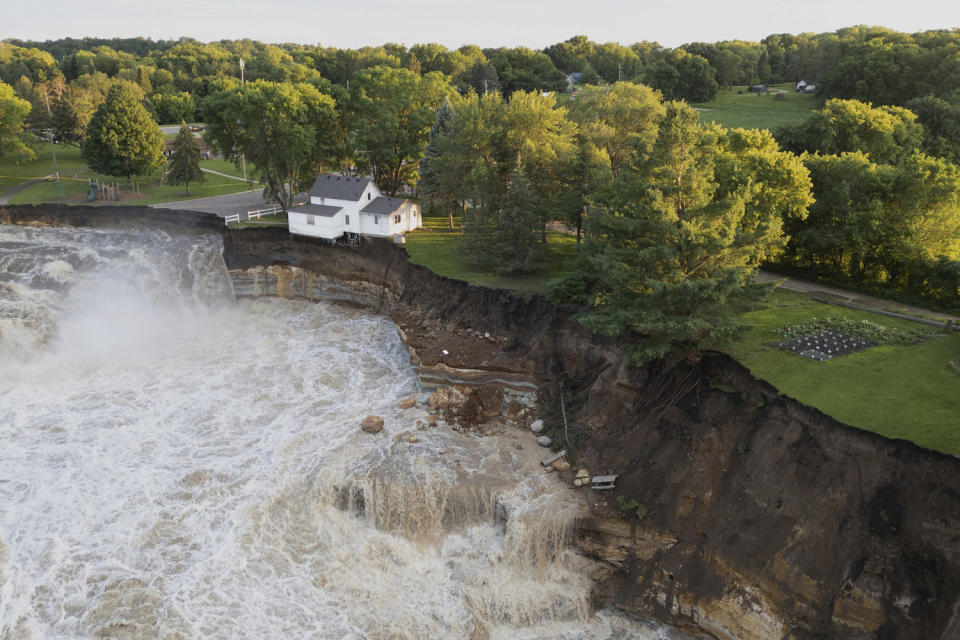


The partial dam failure occurred after three days of heavy rains that left the Minnesota River at its third highest flood height since at least 1881, according to Brennan Dettmann, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service based in the Twin Cities.
In the Mankato area, where the dam is located, 7 to 8 inches of rain fell over three days, based on an analysis by Kenny Blumenfeldsenior climatologist at the Minnesota State Climate Office.
“That elbow of the Minnesota River got hit really hard,” he said, adding that in southern Minnesota, rains that heavy would have between a 0.5% and 2% chance of happening each year.
Bill McCormick, who led Colorado’s dam safety program from 2011 to 2021, said the extreme rains have increased tension across the country.
“We are having more frequent and intense storms that are testing aging infrastructure. Spillways and dams that may not have experienced as many storms in a given year are now experiencing more storms,” he said. “All these old systems are being tested more and more.”
Housing development is also increasing danger levels for some dams, McCormick added, as people settle in once-rural areas where dams built for farmland now protect subdivisions.
Hiba Baroud, assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering at Vanderbilt University, said the partial failure of the Rapidan, among others, should prompt lawmakers to take a hard look at how to bolster dam infrastructure and marshalling repairs.
“We really need to think proactively to project potential scenarios for all dams in the U.S. and start prioritizing which dams need to be rehabilitated or improved to avoid a situation like this,” she said, “instead of witnessing a major event and using that as a warns about this particular dam.”
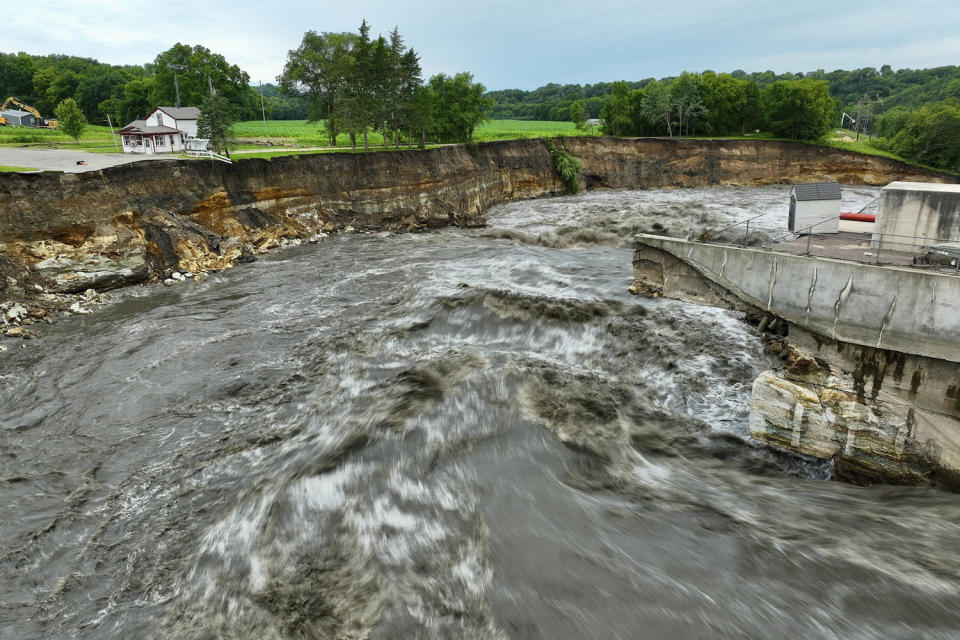


From 2013 to 2023, 283 dams in the U.S. experienced some type of failure, according to data provided by the Association of State Dam Safety Officials and analyzed by NBC News. Some did not cause considerable problems, but others had serious consequences. In 2019, a blizzard precipitated a dam break that destroyed a Nebraska man’s homedrowning him.
Tapia said dam rehabilitation is often limited by insufficient funding and lengthy environmental licensing processes.
“They are taking a long time to fix because of funding and licensing issues,” she said. “Engineering is usually the easiest part.”
This article was originally published in NBCNews. with




































